Speed test of ‘tunneling’ electrons challenges alternative interpretation of quantum mechanics
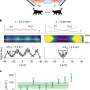
Quantum mechanics describes the unconventional properties of subatomic particles, like their ability to exist in a superposition of multiple states, as popularized by the Schrödinger’s cat analogy, and ability to slip through barriers, a phenomenon known as quantum tunneling.Quantum Physics NewsRead More